ESP8266 and 8051 MCU: A Comprehensive Guide to Integration and Applications
Introduction
The world of microcontrollers (MCUs) is vast and varied, with architectures ranging from the ancient to the cutting-edge. Two names that often surface in discussions about embedded systems and IoT are the ESP8266 and the 8051 MCU. At first glance, they seem to belong to entirely different eras of technology. The 8051, introduced by Intel in 1980, is an 8-bit MCU that has been the bedrock of countless embedded systems for decades. In contrast, the ESP8266, developed by Espressif Systems, is a modern, Wi-Fi-enabled system-on-a-chip (SoC) that helped democratize Internet of Things (IoT) development. While one is a classic workhorse, the other is a connectivity powerhouse. However, the true potential for innovation often lies not in choosing one over the other, but in understanding how to make them work together. This article explores the architectures of both chips, details the methods for their integration, and highlights compelling applications where their combined strengths create robust and cost-effective solutions. For engineers and hobbyists seeking the right components for such integrations, platforms like ICGOODFIND offer a streamlined component sourcing experience, connecting them with reliable suppliers worldwide.

Part 1: Understanding the Individual Architectures
To appreciate how the ESP8266 and 8051 can collaborate, one must first understand their fundamental differences and inherent strengths.
The Legacy and Simplicity of the 8051 MCU
The 8051 microcontroller is an industry legend. Its longevity is a testament to its elegant and effective design. As an 8-bit MCU, it processes data in 8-bit chunks, which is sufficient for a vast array of control-oriented tasks.
- Core Architecture: The classic 8051 core features a CISC (Complex Instruction Set Computer) architecture with a limited set of registers. Its operation is straightforward, making it relatively easy to program in assembly or C.
- On-Chip Peripherals: A typical 8051 includes essential peripherals integrated into the chip, such as:
- 4 KB of ROM (or Flash in modern variants) for program storage.
- 128 Bytes of RAM for data.
- Four 8-bit I/O Ports for interfacing with sensors, LEDs, and other devices.
- Two 16-bit Timers/Counters.
- A full-duplex UART (Serial Port) for asynchronous communication.
- Key Strengths: The primary advantages of the 8051 are its low power consumption, exceptional cost-effectiveness for simple tasks, and a massive existing codebase and knowledge pool. It excels in applications where a dedicated, reliable controller is needed without the overhead of complex operating systems or networking stacks. Its simplicity makes it predictable and robust for real-time control applications.
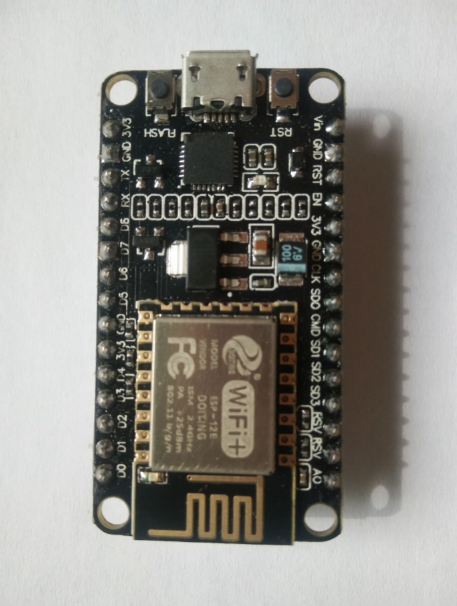
The Modern Power of the ESP8266
The ESP8266 burst onto the scene and single-handedly changed the IoT landscape by offering integrated Wi-Fi at an unprecedented low cost. It is far more than just a microcontroller; it’s a highly integrated SoC.
- Core Architecture: At its heart lies a Tensilica L106 32-bit RISC processor, capable of running at 80 MHz or 160 MHz. This gives it significantly more processing power than the 8051. It is often used with an SDK (Software Development Kit) or frameworks like Arduino to manage its capabilities.
- Integrated Wi-Fi: This is its defining feature. The chip includes a full TCP/IP protocol stack, allowing it to connect to 802.11 b/g/n Wi-Fi networks out of the box. It can function as a station (connecting to a router), an access point (creating its own network), or both simultaneously.
- Generous Memory: Compared to the 8051, the ESP8266 is lavish with memory. It typically includes tens of kilobytes of RAM and megabytes of flash memory, allowing it to store complex programs and web pages.
- Key Strengths: The undeniable strength of the ESP8266 is its built-in Wi-Fi connectivity. Additionally, its superior processing power and ample memory make it suitable for tasks that would be impossible for a standalone 8051, such as serving web pages, parsing JSON data from APIs, or handling secure connections.
Part 2: Bridging the Gap - Methods of Integration
While the ESP8266 is powerful enough to handle both control and connectivity tasks on its own, there are compelling reasons to pair it with an 8051. The main challenge is establishing effective communication between them. The most common and practical method is using asynchronous serial communication (UART).
UART: The Universal Bridge
UART is a simple, widely supported communication protocol that is perfect for this kind of inter-MCU communication. Both the ESP8266 and virtually all modern 8051 variants have at least one UART peripheral.
How it Works:
- Physical Connection: The TX (transmit) pin of the 8051’s UART is connected to the RX (receive) pin of the ESP8266’s UART, and vice-versa. A common ground (GND) connection is essential.
- Protocol Design: A communication protocol must be designed. This is typically a simple packet-based structure where data is framed with start and end markers. For example:
[START_BYTE][COMMAND][DATA_LENGTH][DATA...][CHECKSUM][END_BYTE]- The 8051 gathers sensor data and packages it into this format, then sends it to the ESP8266.
- The ESP8266 parses the packet, verifies the checksum, and then acts on the command—for instance, by sending the data to a cloud server via Wi-Fi.
- Data Flow Scenarios:
- Uplink (Sensor to Cloud): The 8051 reads a temperature sensor -> Packages the data -> Sends it via UART to the ESP8266 -> The ESP8266 connects to Wi-Fi -> Transmits the data to ThingSpeak or AWS IoT.
- Downlink (Cloud to Actuator): A user sends a command via a mobile app -> The cloud server sends it to the ESP8266 -> The ESP8266 receives it via Wi-Fi -> Repackages it and sends a UART command to the 8051 -> The 8051 parses the command and turns on an LED or motor.
This division of labor leverages the best of both worlds: the real-time I/O control and low-power operation of the 8051, combined with the high-performance networking capabilities of the ESP8266.
Alternative Communication Methods
While UART is the most straightforward method, other options exist: * SPI (Serial Peripheral Interface): A faster, synchronous serial protocol. It requires more pins (SCK, MOSI, MISO, SS) but offers higher data transfer rates, which could be useful for streaming data. * I2C (Inter-Integrated Circuit): A two-wire serial protocol that supports multiple devices on the same bus. This could be useful if multiple 8051s (as slave devices) need to report to a single ESP8266 (as master).
For developers implementing these complex communication bridges, finding MCUs with robust and well-documented peripheral interfaces is crucial. This is where a specialized component sourcing platform proves invaluable. By using a service like ICGOODFIND, engineers can quickly locate and compare various 8051 derivatives and ESP8266 modules from different manufacturers, ensuring they get components that meet their specific voltage level, pinout, and performance requirements for a seamless integration.
Part 3: Practical Applications and Project Ideas
The synergy between the ESP8266’s connectivity and the 8051’s control prowess opens up numerous practical applications.
1. Smart Agriculture and Environmental Monitoring
In large-scale farms or greenhouses, multiple sensor nodes are needed. * Implementation: Each node uses a low-power 8051 MCU to continuously monitor soil moisture, humidity, and temperature. The 8051 can sleep most of the time to conserve battery power, waking up only for readings. It then wakes up the ESP8266 module only when it’s time to transmit data. The ESP8266 connects to a central gateway and sends the aggregated sensor data. * Benefit: This architecture dramatically reduces overall power consumption because the power-hungry Wi-Fi radio is active only for short bursts, while the efficient 8051 handles all sensor polling.
2. Industrial Control and HMI (Human-Machine Interface)
Legacy industrial machinery often uses 8051-family controllers. * Implementation: An ESP8266 can be added as a “connectivity co-processor” to an existing 8051-based system. The 8051 continues its real-time control tasks (e.g., reading limit switches, controlling motors). The ESP8266 provides a web-based HMI. An operator can use a smartphone or computer to connect to the ESP8266’s web server, view machine status (sent from the 8051 via UART), and send commands (e.g., “start cycle,” “change speed”). * Benefit: This modernizes legacy equipment without a costly full-system redesign, adding remote monitoring and control capabilities.
3. Home Automation and Security Systems
A multi-zone security or automation system can benefit from this distributed approach. * Implementation: Several low-cost 8051 boards can be placed around a house as “satellite nodes,” each controlling a few window/door sensors, motion detectors, or light actuators in one room or zone. A central ESP82666 acts as the hub. The satellite nodes report their status to the hub via UART (or even wired serial over longer distances). The hub aggregates all this data and connects to the home router, allowing users to check their home’s status from anywhere in the world. * Benefit: Cost savings by using simple MCUs for localized tasks and one powerful MCU for centralized networking logic. It also improves reliability through system modularity.
Conclusion
The ESP8266 and the 8051 MCU represent two distinct generations of microcontroller technology, yet they are far from mutually exclusive. The venerable 8051 remains a highly viable solution for tasks demanding straightforward control, low power, and minimal cost. Conversely, the ESP8266 is an undisputed champion of IoT connectivity, packing impressive computational resources into a tiny package. By integrating these two components—primarily through a simple UART bridge—developers can architect systems that are greater than the sum of their parts. This hybrid approach allows engineers to allocate tasks optimally: real-time control and sensor management to the robust 8051, and complex networking and data processing to the powerful ESP8266. For those embarking on such projects, sourcing reliable components is a critical first step. Platforms like ICGOODFIND simplify this process by providing access to a wide range of MCUs and modules, ensuring that your innovative designs are built on a foundation of quality components.