What Functions Can 8051 MCU Realize?
Introduction
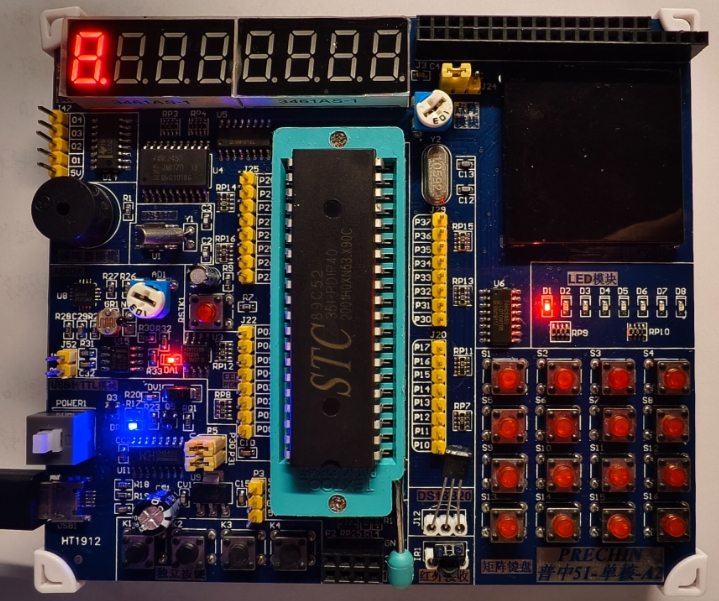
The 8051 microcontroller, introduced by Intel in 1980, remains one of the most influential and widely-used microcontroller architectures in the embedded systems world. Despite being over four decades old, its simple yet powerful design continues to power countless applications across industries. The enduring popularity of the 8051 MCU stems from its versatile architecture that enables developers to implement diverse functionalities with minimal components. From simple LED blinking circuits to complex industrial automation systems, the 8051 has proven its capabilities across generations of electronic devices. This article explores the extensive range of functions that can be realized using the 8051 microcontroller, demonstrating why it remains relevant in today’s rapidly evolving technological landscape and how platforms like ICGOODFIND continue to support developers working with this timeless architecture.

Main Body
Fundamental Operational Capabilities
The 8051 microcontroller’s architecture provides a robust foundation for implementing various basic and intermediate electronic functions. At its core, the 8051 contains a CPU, RAM, ROM, I/O ports, and timers/counters all integrated into a single chip, creating a complete microcomputer system capable of standalone operation.
Digital I/O Operations form the most fundamental capability of the 8051 microcontroller. The standard 8051 features four 8-bit bidirectional I/O ports (P0, P1, P2, and P3), providing 32 I/O lines that can be configured as inputs or outputs through software. These ports enable the microcontroller to interface with external devices such as sensors, switches, LEDs, relays, and displays. Each port can source or sink current, allowing direct connection to various peripherals without additional interface circuitry in many applications. The flexibility of these I/O ports means developers can create custom interfaces for specific applications, from reading button inputs to controlling motor drivers.
Timer and Counter Functions represent another critical capability of the 8051 architecture. The microcontroller typically includes two or three 16-bit timer/counters that can be programmed to operate in different modes. These timers can function as interval timers to generate precise time delays, event counters to count external pulses, or baud rate generators for serial communication. The timer functions are essential for implementing real-time operations where precise timing is crucial, such as in data logging systems, waveform generation, or periodic sensor reading applications. The ability to generate interrupts on timer overflow further enhances the real-time capabilities of the 8051, allowing time-critical tasks to be handled efficiently.
Serial Communication Capabilities enable the 8051 to communicate with other microcontrollers, computers, or peripheral devices. The built-in Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter (UART) supports full-duplex serial communication, allowing simultaneous transmission and reception of data. This capability facilitates interfaces with RS-232, RS-485, and other serial communication standards commonly used in industrial environments. Additionally, the 8051 can be programmed to implement other serial protocols such as SPI and I2C through bit-banging techniques using its general-purpose I/O pins. These communication functions make the 8051 suitable for distributed systems where multiple devices need to exchange data.
Interrupt Handling Mechanism provides the 8051 with responsive event management capabilities. The architecture supports multiple interrupt sources including external interrupts, timer interrupts, and serial port interrupts. Each interrupt can be individually enabled or disabled and assigned different priority levels. This interrupt system allows the microcontroller to respond promptly to external events without continuous polling, making it efficient for applications requiring quick response to critical events. The interrupt capability is particularly valuable in control systems where immediate action must be taken when certain conditions are detected, such as safety limits being exceeded or emergency stop signals being activated.
Advanced Application Implementations
Beyond basic operations, the 8051 microcontroller can be programmed to implement sophisticated applications across various domains. Its balanced combination of processing power, peripheral integration, and low power consumption makes it suitable for numerous advanced implementations.
Industrial Control and Automation Systems represent a significant application area for the 8051 microcontroller. In these environments, the 8051 can perform functions such as PID controller implementation for precise process control, data acquisition from multiple sensors, and actuator control for motors and valves. The microcontroller’s deterministic operation and reliable performance under industrial conditions make it ideal for these critical applications. Additionally, the 8051 can implement communication protocols like Modbus for integration into larger industrial networks, enabling seamless data exchange with supervisory control systems. The robustness of the architecture ensures stable operation even in electrically noisy industrial environments.
Consumer Electronics Applications extensively utilize the 8051 microcontroller due to its cost-effectiveness and adequate processing capabilities. In this domain, the 8051 can realize functions such as remote control signal processing, display interface management for LCDs and LEDs, user input handling from keypads and touch interfaces, and power management in battery-operated devices. Many home appliances including washing machines, microwave ovens, air conditioners, and television remote controls employ 8051-based control systems. The microcontroller’s ability to interface with various sensors and peripherals while maintaining low power consumption makes it particularly suitable for portable and energy-efficient consumer products.
Automotive Electronics Systems have historically relied on the 8051 architecture for various functions. While modern vehicles use more powerful microcontrollers for advanced features, the 8051 still finds application in basic control units, sensor interface modules, and simple actuator controllers. Functions such as window control, seat positioning, basic instrument cluster operations, and simple entertainment system controls can be efficiently implemented using the 8051. The automotive industry’s stringent reliability requirements are met by the 8051’s proven stability and the availability of automotive-grade variants that operate across the required temperature ranges.
Communication Devices and Protocols represent another advanced application area where the 8051 demonstrates its versatility. The microcontroller can be programmed to implement various communication protocol stacks including TCP/IP for basic network connectivity, wireless communication interfaces for Bluetooth and Zigbee modules, and data encoding/decoding algorithms for specialized communication systems. While the 8051 may not handle high-speed communications directly, it can effectively manage communication controllers and process protocol data. This capability enables the development of networked devices for Internet of Things (IoT) applications, where the 8051 serves as the central controller coordinating communication between sensors, actuators, and network interfaces.
Specialized Function Realizations
The programmability of the 8051 microcontroller allows developers to implement specialized functions tailored to specific application requirements. Through creative programming and appropriate peripheral interfacing, the 8051 can perform tasks beyond its original design intentions.
Signal Processing Applications can be implemented on the 8051 despite its limited processing power compared to modern digital signal processors. The microcontroller can perform basic digital filter implementations such as FIR and IIR filters for signal conditioning, FFT algorithms for frequency domain analysis of signals, and waveform generation for testing and measurement applications. While these implementations may not match the performance of dedicated DSP chips for high-speed applications, they are entirely adequate for many embedded systems where processing requirements are modest. The key advantage is achieving signal processing capabilities without additional hardware components, reducing system cost and complexity.
Security and Access Control Systems represent another specialized application domain where the 8051 finds extensive use. The microcontroller can implement encryption and decryption algorithms for data security, authentication protocols for user verification, and biometric sensor interfaces for advanced access control. Functions such as keypad code verification, RFID card reading, fingerprint matching, and electronic lock control can all be realized using the 8051 architecture. The security of these systems is enhanced by the 8051’s ability to operate in protected modes that prevent unauthorized access to program memory and critical data.
Measurement and Instrumentation Systems benefit from the 8051’s analog interfacing capabilities when combined with external ADCs. The microcontroller can implement precision measurement algorithms for sensors including thermocouples, strain gauges, and pressure transducers, calibration routines to compensate for sensor non-linearities and environmental factors, and data logging functionalities with time-stamping capabilities. The timer/counter modules can be configured for frequency measurement, pulse width measurement, and period measurement applications with surprisingly high accuracy. These capabilities make the 8051 suitable for developing dedicated test equipment and embedded measurement subsystems.
When implementing these specialized functions through platforms like ICGOODFIND, developers gain access to comprehensive resources including code libraries, application notes, and development tools that significantly accelerate the implementation process while ensuring reliability.
Conclusion
The 8051 microcontroller continues to demonstrate remarkable versatility more than four decades after its introduction, capable of realizing an extensive range of functions from basic digital I/O operations to sophisticated application-specific implementations. Its enduring relevance in the embedded systems landscape is a testament to its well-balanced architecture that provides adequate processing power, comprehensive peripheral integration, and low power consumption at a competitive cost point. While modern microcontrollers offer higher performance and more advanced features, the 8051 remains perfectly suited for countless applications where its capabilities align perfectly with requirements.
The continued support from manufacturers producing enhanced 8051-compatible variants and resources available through platforms like ICGOODFIND ensures that developers can leverage this proven architecture efficiently. These resources provide documentation.