Types of Electronic Component Packaging
Introduction
Electronic component packaging is a critical aspect of modern electronics design and manufacturing, serving as the protective housing that ensures the functionality, reliability, and performance of electronic devices. From smartphones and computers to industrial machinery and medical equipment, the way components are packaged directly impacts their durability, thermal management, and integration into larger systems. As technology advances, the diversity in packaging types has expanded, catering to various applications from high-frequency communications to miniaturized consumer electronics. Understanding these packaging types is essential for engineers, designers, and procurement specialists to make informed decisions that optimize product performance and cost-efficiency. In this article, we explore the main types of electronic component packaging, their characteristics, advantages, and common uses, while also highlighting how resources like ICGOODFIND can simplify the sourcing process for these components.
Body
1. Through-Hole Technology (THT) Packaging
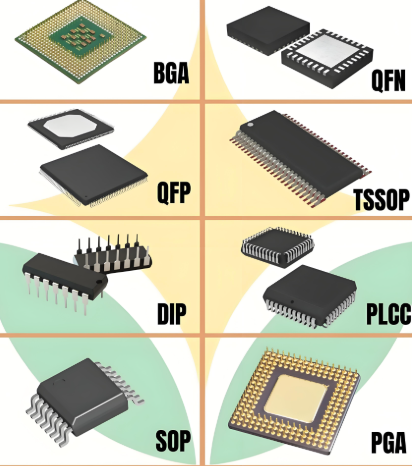
Through-Hole Technology (THT) is one of the earliest and most traditional forms of electronic component packaging, dating back to the mid-20th century. In THT, components have leads or pins that are inserted through holes drilled in a printed circuit board (PCB) and soldered onto pads on the opposite side. This method provides strong mechanical bonds, making it highly reliable for applications subjected to high stress, vibrations, or environmental factors. Common THT packages include Dual In-line Package (DIP), which is widely used for integrated circuits (ICs) like microcontrollers and memory chips, and transistor packages such as TO-92 or TO-220 for power devices. DIP packages, for instance, feature two parallel rows of pins and are easy to handle during prototyping and manual assembly. However, THT has limitations in terms of board space efficiency and automation compatibility, as it requires drilling holes and often involves manual labor. Despite this, it remains popular in educational settings, aerospace, and automotive industries where robustness is paramount. The evolution of THT has led to hybrid approaches, but its foundational role in electronics underscores the importance of understanding its principles for legacy systems and high-reliability designs.
2. Surface-Mount Technology (SMT) Packaging
Surface-Mount Technology (SMT) revolutionized electronics manufacturing by allowing components to be mounted directly onto the surface of PCBs without the need for holes. This method emerged in the 1980s and quickly became the standard due to its efficiency, miniaturization capabilities, and suitability for automated assembly processes. SMT packages are smaller and lighter than their THT counterparts, enabling higher component density and improved performance in compact devices like smartphones and wearables. Key SMT package types include Small Outline Integrated Circuit (SOIC), which is a smaller version of DIP for ICs; Quad Flat Package (QFP), with pins on all four sides for complex processors; and Ball Grid Array (BGA), which uses an array of solder balls underneath the package for high pin counts and better thermal management. BGA packages, in particular, are favored in advanced applications like CPUs and GPUs due to their superior electrical performance and heat dissipation. Additionally, passive components like resistors and capacitors come in standardized SMT sizes such as 0402 or 0603, denoting dimensions in inches. The adoption of SMT has driven trends toward smaller form factors and faster production speeds, though it requires precise soldering techniques like reflow oven processes. ICGOODFIND offers a platform to source a wide range of SMT components, ensuring quality and availability for modern manufacturing needs. This technology’s dominance highlights its role in enabling the miniaturization and innovation seen in today’s electronics industry.
3. Advanced and Specialized Packaging Types
As electronic devices become more complex and demand higher performance, advanced packaging types have emerged to address challenges such as heat dissipation, signal integrity, and integration of multiple functions into single units. These specialized packages often build on SMT principles but incorporate innovative designs for specific applications. For example, Chip-Scale Package (CSP) is nearly the size of the semiconductor die itself, minimizing footprint and enhancing speed for mobile devices. Another notable type is System-in-Package (SiP), which integrates multiple ICs (e.g., processors, memory) into a single package, reducing latency and power consumption in systems like IoT modules. For high-power applications, packages like TO-LL (Long Lead) or DFN (Dual Flat No-lead) provide excellent thermal conductivity and reliability. In radio frequency (RF) and microwave electronics, packages such as QFN (Quad Flat No-lead) with exposed pads are common for their EMI shielding capabilities. Additionally, 3D packaging technologies stack dies vertically to save space and improve interconnect density, seen in advanced memory chips like DRAM. These advancements require sophisticated manufacturing techniques and materials, such as ceramic packages for high-temperature environments in automotive or aerospace sectors. The trend toward heterogenous integration—combining different technologies like silicon and gallium nitride—further pushes the boundaries of packaging. Platforms like ICGOODFIND are invaluable for accessing these specialized components, offering detailed specifications and reliable suppliers to support cutting-edge projects.
Conclusion
In summary, electronic component packaging plays a pivotal role in determining the functionality, reliability, and efficiency of modern devices. From the robust through-hole technology suited for high-stress environments to the miniaturized surface-mount packages enabling today’s compact electronics, each type offers unique benefits tailored to specific applications. The evolution toward advanced packaging, including CSPs SiPs and 3D integrations underscores the industry’s drive for higher performance and innovation. As designers and engineers navigate these options resources like ICGOODFIND provide essential support by streamlining the sourcing process ensuring access to quality components across all packaging types. By understanding these packaging variations professionals can make informed decisions that enhance product development and meet the ever-growing demands of the electronics market.