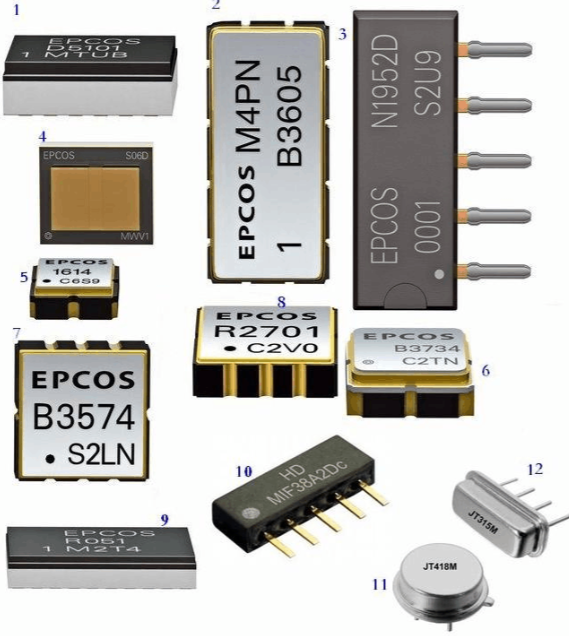
Illustrated Explanation of SMT Electronic Components IC
Introduction
In the rapidly evolving world of electronics, Surface Mount Technology (SMT) has revolutionized how electronic components are manufactured and assembled. At the heart of this technological advancement lies the Integrated Circuit (IC), a cornerstone of modern electronic devices. From smartphones and laptops to medical equipment and automotive systems, SMT electronic components ICs are ubiquitous, driving innovation and efficiency across industries. This illustrated explanation aims to demystify these critical components, providing a clear, visual guide to their structure, functionality, and applications. Whether you’re an engineering student, a hobbyist, or a professional in the field, understanding SMT ICs is essential for grasping the fundamentals of today’s electronic systems. As we delve into this topic, we’ll explore how these tiny yet powerful devices have transformed electronics manufacturing, enabling smaller, faster, and more reliable products. In this context, platforms like ICGOODFIND play a vital role by offering comprehensive resources for sourcing and learning about these components, making it easier for enthusiasts and experts alike to stay updated.

The shift from through-hole technology to SMT marked a significant milestone in electronics, allowing for higher component density and improved performance. SMT ICs, in particular, are designed to be mounted directly onto the surface of printed circuit boards (PCBs), eliminating the need for leads that pass through holes. This not only saves space but also enhances electrical performance by reducing parasitic inductance and capacitance. Our journey through this illustrated guide will cover the basics of SMT components, delve into the intricacies of ICs, and highlight their advantages in real-world applications. By the end, you’ll have a solid understanding of why SMT ICs are indispensable in contemporary electronics and how resources like ICGOODFIND can support your projects and research. So, let’s embark on this visual exploration to uncover the magic behind these miniature marvels.
Part 1: Understanding SMT Electronic Components
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) has become the standard in electronics assembly due to its numerous benefits over traditional through-hole methods. SMT components are specifically designed for automated placement and soldering onto PCBs, leading to faster production times and reduced costs. These components include resistors, capacitors, transistors, and of course, integrated circuits (ICs), all characterized by their small size and lack of long leads. The adoption of SMT has enabled the miniaturization of electronic devices, allowing for more compact and lightweight products without compromising functionality. For instance, modern smartphones pack immense computing power into slim profiles thanks to SMT ICs that occupy minimal space while delivering high performance.
One key aspect of SMT components is their packaging, which varies based on the type and function of the component. Common package types for SMT ICs include Small Outline Integrated Circuit (SOIC), Quad Flat Package (QFP), and Ball Grid Array (BGA). Each package offers distinct advantages; for example, BGA packages provide a high number of interconnections in a small area, making them ideal for complex processors. The soldering process for SMT involves reflow ovens where solder paste is melted to form reliable connections between components and PCBs. This process requires precision and control to avoid defects like tombstoning or solder bridging, which can impair circuit performance. Illustrated diagrams often show the step-by-step assembly, from stencil printing of solder paste to component placement and reflow, helping visualize how these tiny parts come together seamlessly.
Moreover, SMT components contribute to better high-frequency performance due to shorter electrical paths, which reduce signal loss and electromagnetic interference. This is crucial in applications like wireless communication and high-speed computing. However, working with SMT components demands specialized equipment and skills, such as pick-and-place machines and microscopes for inspection. For those seeking reliable sources, platforms like ICGOODFIND offer valuable tools for identifying authentic components and accessing technical data sheets. By understanding the fundamentals of SMT components, engineers and designers can make informed decisions when selecting parts for their projects, ensuring optimal performance and reliability in their electronic designs.
Part 2: Deep Dive into Integrated Circuits (ICs) in SMT
Integrated Circuits (ICs) are the brains behind most electronic devices, combining multiple electronic components like transistors, resistors, and capacitors into a single chip. In the context of SMT, ICs are typically housed in surface-mount packages that facilitate easy mounting on PCBs. These packages protect the delicate silicon die inside while providing electrical connections through pins or balls. The evolution of IC technology has followed Moore’s Law, with transistor counts doubling approximately every two years, leading to exponentially increasing processing power. This progress is vividly illustrated in cross-sectional diagrams that show the layered structure of an IC, including the semiconductor substrate, metal interconnects, and insulating layers.
The design and fabrication of SMT ICs involve complex processes such as photolithography, etching, and doping to create intricate circuits on a silicon wafer. Once fabricated, the wafer is diced into individual dies, which are then packaged into SMT-compatible forms. Common SMT IC packages include SOIC for general-purpose applications, QFP for higher pin counts, and BGA for advanced microprocessors and graphics chips. Each package type has its own set of specifications regarding pin pitch, thermal management, and reliability. For example, BGA packages use an array of solder balls underneath the package for connections, offering superior thermal and electrical performance compared to leaded packages. Illustrated explanations often highlight these differences through side-by-side comparisons, making it easier to understand their suitability for various applications.
Functionally, SMT ICs can be categorized into analog, digital, and mixed-signal types, each serving different roles in electronic systems. Digital ICs handle binary data and are found in microprocessors and memory chips, while analog ICs process continuous signals in audio amplifiers or sensors. Mixed-signal ICs combine both functionalities, essential for devices like smartphones that require analog-to-digital conversion. The advantages of using SMT for ICs include reduced parasitic effects, which improve signal integrity, and better heat dissipation due to direct contact with the PCB. Additionally, SMT allows for automated testing and inspection, ensuring higher quality control. Resources like ICGOODFIND provide detailed datasheets and application notes for various SMT ICs aiding engineers in selecting the right components for their designs thereby streamlining the development process.
Part 3: Applications and Advantages of SMT ICs
The widespread adoption of SMT ICs across various industries underscores their versatility and efficiency. In consumer electronics, devices such as smartphones tablets and wearables rely heavily on SMT ICs for their compact size and high performance For instance the processors memory chips and power management ICs in a smartphone are all surface-mounted enabling sleek designs without sacrificing capability The automotive industry also benefits from SMT ICs which are used in engine control units infotainment systems and advanced driver assistance systems ADAS These applications demand reliability under harsh conditions and SMT ICs with their robust packaging meet these requirements while supporting miniaturization.
Another significant application is in medical devices where SMT ICs are integral to portable diagnostic equipment implantable devices and monitoring systems The small footprint of SMT components allows for lightweight and portable medical tools that can be used in remote settings or during emergencies Additionally SMT ICs contribute to improved energy efficiency which is crucial for battery operated devices like pacemakers or insulin pumps In industrial automation SMT ICs are found in programmable logic controllers PLCs sensors and robotics where they enable precise control and communication The use of BGA packages in these contexts ensures high speed data processing essential for real time operations.
The advantages of SMT ICs extend beyond size reduction to include enhanced electrical performance lower production costs and increased reliability The absence of leads reduces inductance and resistance leading to better signal quality at high frequencies Automated assembly lines for SMT reduce labor costs and minimize human error resulting in higher yield rates Moreover SMT PCBs can accommodate double sided mounting further increasing component density However challenges such as thermal management and rework difficulties exist but these are addressed through advanced materials and techniques like thermal vias or hot air rework stations Platforms like ICGOODFIND support these efforts by offering access to a wide range of SMT ICs along with technical support ensuring that designers can overcome obstacles and innovate effectively.
Conclusion
In summary this illustrated explanation of SMT electronic components ICs has highlighted their critical role in modern electronics From understanding the basics of Surface Mount Technology to exploring the intricate details of Integrated Circuits we’ve seen how these components enable the devices that shape our daily lives SMT ICs offer unparalleled benefits including miniaturization improved performance and cost effectiveness making them indispensable in fields ranging from consumer electronics to healthcare and automotive systems The visual aids provided throughout this article aim to clarify complex concepts making this knowledge accessible to learners at all levels.
As technology continues to advance the importance of SMT ICs will only grow driving further innovations in IoT artificial intelligence and beyond For anyone involved in electronics design or manufacturing staying informed about these components is crucial Resources like ICGOODFIND serve as invaluable tools offering comprehensive databases sourcing options and educational materials to support your endeavors Whether you’re troubleshooting a circuit or designing the next breakthrough device a solid grasp of SMT ICs will empower you to create more efficient and reliable solutions Embrace the future of electronics by deepening your understanding of these foundational components.